See the common situations of CNC machining: tedious set-up, accumulated scrap, long CNC machining man-hours.
As an engineer, what do you think of? I have been addicted to cost reduction design for so long that when I saw this situation, the picture that came to my mind was: how much does it cost!
This piece of scrap is bought back with money, and the high-speed rotating knives rotate in circles is the expenditure of money. good! Among the many CNC parts machining processes, CNC machining should be one of the most expensive. This article will introduce 16 cost-reducing design tips for CNC machining.

Factors of machining cost in CNC machining factory:
1) CNC machining time
The longer the CNC machining time, the higher the CNC machining cost. CNC machining time is a major driver of CNC machining costs.
2) Material cost
Billet material cost is an important part of CNC machining cost. Material costs can be reduced through optimized design to maximize the use of standardized blanks and to reduce scrap.
3) Installation time
When the batch size is small, the preparation of the geometric model and the planning of the CNC machining process seriously affect the CNC machining cost. This part of the cost is a fixed cost, and the CNC machining factory can share it through large-scale CNC machining production.
4) Other design factors
When CNC part design has special requirements (such as close tolerance requirements and thin wall design), special tools, more precise quality control, lower CNC machining speed, and more complex CNC machining steps are required, which can seriously affect CNC machining cost.
When we understand the cost drivers of CNC machining, we can take corresponding cost-reducing design measures to reduce CNC machining costs.
1. Rounding at the inner vertical right angle
All CNC machining tools have a cylindrical shape. When CNC machining the groove body, a rounded corner that is consistent with the shape will be generated at the connection between the vertical surface and the surface of the groove body.
If the fillet at the connection of the vertical surface of the groove body is too small in the product design, a small tool needs to be used, which means that the CNC machining time will increase, because the machining efficiency of the small tool is not as good as that of the large tool – this will lead to CNC machining. Increased machining time and cost.
To reduce costs:
1. The fillet size should be at least 1/3 of the groove depth, the bigger the better;
2. All fillets have the same size; so that the same tool can be used for the entire CNC machining;
3. At the root of the groove body, design a small rounded corner (0.5mm or 1mm), or not rounded;
4. The ideal fillet size should be slightly larger than the radius of the tool, which will reduce the load on the tool during CNC machining, thereby reducing the machining cost. For example, if the depth of the groove body is 12mm, and the rounded corners are designed to be 5mm or more, a tool with a diameter of 8mm (radius of 4mm) can be used in CNC machining, which can ensure the efficiency of CNC machining;
5. If it cannot be rounded due to design requirements, for example, it needs to be matched with another square part, in order to avoid small rounded corners.
2. Reduce the depth of the groove
The CNC machining of the groove greatly affects the cost of the part, because a large amount of material needs to be machined to remove, which can greatly increase the CNC machining time.
The machining depth of CNC tools is limited. When the depth of the groove is 2~3 times the diameter of the tool, the machining performance is the best. For example, a milling cutter with a diameter of 12mm can machine a groove with a safe depth of up to 25mm.
Of course, it is also possible for a CNC shop to machine deeper grooves, up to 4 times the tool diameter, but this adds to the cost, especially when using a multi-axis CNC machine.
To reduce costs: the depth of the tank body does not exceed 4 times the length.
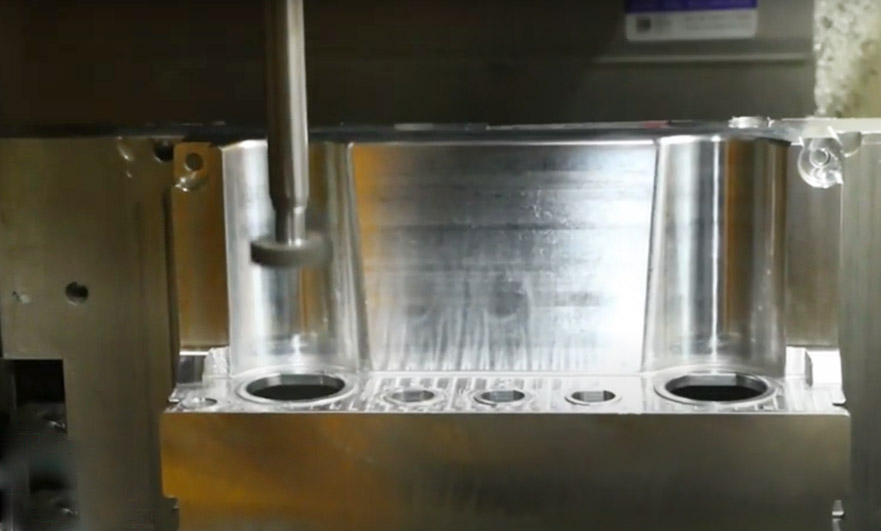

3. Avoid thin walls
Unless otherwise required, thin-wall designs should be avoided because of their insufficient strength and high CNC machining costs.
Thin-walled CNC machining is easy to deform or even break. In order to avoid this situation, CNC machining factories need to add more complex CNC machining paths, which will consume more CNC machining man-hours. Thin walls are more prone to vibration, and machining thin walls with high precision is a big challenge.
CNC machining factory to reduce costs:
1. For metal CNC parts, the thickness of the wall is at least 0.8mm, the thicker the better;
2. For plastic CNC parts, the thickness of the wall should be at least 1.5mm, the thicker the better;
3. The minimum size of metal parts can be 0.5mm, and the minimum size of plastic parts can be 1mm. Of course, this is not recommended;
Thin walls are often present when designing holes (both through and screw holes) or slots at the edges of CNC parts and need to ensure that the above design guidelines are followed.
Avoid thin walls to reduce CNC machining time
4. Reduce the thread depth
Unnecessary thread depths increase machining costs in CNC machining shops because special tools are required.
Remember: too long a thread depth (more than 3 times the hole diameter) will not increase the strength of the connection.
To reduce costs:
1. The thread depth can be up to 3 times the diameter of the screw hole.
2. For blind hole tapping, it is best for CNC machining parts factory to add at least 1/2 extra length of hole thread diameter at the root of the hole.
5. Design standard size holes
Using standard drills, holes can be machined quickly and accurately; for non-standard holes, using end mills will increase the cost.
Also, the depth of the hole should not exceed 4 times its diameter. Deep holes (Z more than 10 times the diameter) can be machined in CNC machined factories, but this will drastically increase the cost because the machining is difficult.
6. Avoid precision tolerance requirements
Close tolerance requirements increase costs because they require complex CNC machining operations, increase CNC machining time, and require more inspections.
Defining dimensional tolerances of parts must be taken seriously, avoiding marking tolerances on any dimension, marking tolerances only when necessary, and marking precision tolerances only as a last resort.
If no tolerances are defined in the CNC part drawing, then the part is machined to standard tolerances (± 0.2mm or more), which is sufficient for most non-critical dimensions, which can significantly reduce CNC machining costs.
For those internal features, close tolerances are more difficult to guarantee. For example, when machining internally intersecting holes or grooves, small defects such as burrs are easy to appear on the edges due to force deformation.
These features require detection and deburring processes, which can only be performed manually, which is costly and time-consuming, resulting in high costs.
To reduce costs:
1. Define close tolerances only as a last resort.
2. All dimensions are marked by the same datum.
3. Remember: the decimal point in the tolerance is important, it defines how accurate it is and which measurement tool needs to be used. For example, two decimal places can be measured using a vernier caliper, and three decimal places can be measured using a micrometer or a CMM. To reduce costs, try to avoid adding unnecessary decimal places.
4. Precision tolerance requirements can be avoided through optimized product design, such as shortening the dimensional chain, using positioning features, etc.
7. Reduce the number of clamping
Minimize the number of clamping of parts as much as possible, preferably only once.
For example, a part with blind holes on both sides needs to be clamped twice, one side is machined and then rotated and re-clamped before the other side can be machined.
Rotating or repositioning parts can add to CNC machining costs, as the clamping action is typically done manually. In addition, for complex part structures, it is necessary to customize the clamping fixture, which further increases the cost. Particularly complex part structures may require a multi-axis CNC machine, further increasing the cost due to the high hourly rates of multi-axis CNC machines.
It is possible to consider dividing the complex part structure into multiple parts for CNC machining, and then tightening them into one body by threading or welding.
To reduce costs:
1. Design parts only need to be clamped once.
2. If it is not possible, divide the complex parts into multiple parts and fasten them into one body through the subsequent process.
8. Avoid small features with large aspect ratios
When CNC machined in a CNC machined parts factory, some small features with large aspect ratios are prone to vibration, making accurate machining difficult.
To avoid this, these small features should be connected with some thicker walls or supported by some stiffeners.
To reduce costs:
1. Avoid designing features with an aspect ratio of more than 4.
2. Small features are connected to thicker walls or stiffeners are added for support.
9. Remove text and symbols on the surface of CNC parts
Text and symbols on the surface of CNC parts can greatly increase the cost of CNC machining, because additional CNC machining operations are required and more CNC machining time is consumed.
Text and symbols can be added to CNC parts using some surface treatment techniques, such as silk screen or spray painting, which is a more cost-effective method.

To reduce costs:
1. Remove the text and symbols on the surface of all parts;
2. If text and symbols are necessary, choose concave rather than convex, as the latter requires more material to be removed.
10. Consider the CNC machining process of the material
The CNC machining manufacturability of a material refers to the difficulty of machining the material.
The better the machining technology of the CNC parts machining factory, the easier the parts are CNC processed, and the cost is lower.
The CNC machinability of a material depends on the physical properties of the material. In general, the softer and more ductile the material, the easier it is to CNC machine.
For example, brass C360 has the highest CNC processability and can be processed at high speed; aluminum alloys (aluminum 6061 and 7075) can also be easily machined.
The processability of steel is very low. Compared with aluminum alloy, steel requires more than twice the machining time. Of course, the processability of different steels is different. The processability index of stainless steel 304 is 45%, while the index of stainless steel 303 is 78%, which is easier to process.
The machining properties of plastic materials depend on their stiffness and thermal properties. During CNC machining, plastic materials are easily melted and deformed at high temperatures.
POM is the easiest material to CNC process, followed by ABS; PEEK and nylon are common engineering plastic materials that are difficult to process.
In order to reduce costs: if possible, try to choose materials with good CNC machining process.
11. Consider the price of raw material billets
Raw material billet price is another key factor in CNC cost.
The table below shows the prices of common metal and plastic raw material blanks with blank dimensions of 150 x 150 x 25 mm.
|
raw materials |
Billet price (values are for comparison only) |
| Aluminum 6061 | ¥170 |
| Aluminum 7075 | ¥540 |
| Stainless steel 304 | ¥610 |
| Stainless steel 303 | ¥1000 |
| Brass C360 | ¥1006 |
| ABS | ¥115 |
| Nylon | ¥204 |
| POM | ¥180 |
| PEEK | ¥2000 |
Aluminum 6061 is obviously a very cost-effective material, not only the billet price is low, but also the CNC machining process is good, which is very suitable for making CNC prototypes.

The CNC machining process of stainless steel 303 and brass C360 is also very good, the CNC machining efficiency is high and the time is short, but the billet price is very high, so it is only suitable for large-scale CNC machining production. Through batch effects, high billet prices are balanced by short machining times.
The price of plastic materials such as ABS, nylon and POM is close to the price of aluminum 6061. However, they are more difficult to machine and therefore CNC cost more. PEEK is a very expensive material and is only used when necessary.
To reduce costs: choose materials with low billet prices as much as possible, especially when proofing.
12. Consider the blank size
Blank size affects CNC machining costs: To ensure dimensional accuracy in CNC parts machining plants, material must be removed from all sides of the part, which can significantly increase material costs, especially in larger batches.
Generally, the blank size is at least 3mm larger than the part. For example, if the external dimension of a part is 30X30X30mm, then the blank with the size of 35X35X35mm can be selected; and the external size is 27X27X27mm, then the blank with the size of 30X30X30mm can be selected, which can save a part of the material cost.
To reduce costs:
1. The blank size is generally at least 3mm larger than the part size.
2. You can consult the CNC machining supplier for standard blank size specifications, and try to design CNC parts close to the blank size specifications to reduce material waste.
13. Avoid multiple surface treatments
Surface treatments can improve the appearance and resistance of CNC parts to harsh environments, but they also increase cost.
If the CNC part requires several different surface treatments, this will increase the cost even more, since it requires more steps, for example some surfaces need to be masked.
To reduce costs:
1. Cancel surface treatment.
2. Avoid multiple surface treatments.
14. Large-scale CNC machining production
In CNC machining, the batch of CNC parts affects the machining cost, because when the batch demand is small, the initial installation cost of CNC machining is allocated to each part is relatively high. When the batch size is large, the installation cost is allocated less to each part.
The larger the batch of CNC machined parts, the lower the CNC cost of the CNC parts machining factory, which is more obvious when the batch of parts is very small: even a small increase in quantity can significantly reduce the cost.
The batch of CNC parts is increased from 1 to 5, and the cost of parts is reduced by more than 50%.
To reduce costs: High-volume production reduces costs, and can place a larger order instead of multiple scattered orders.
15. Design axially symmetrical parts
Axially symmetric parts can be CNC turned or CNC milled at machine hour rates that are much less than 3-axis or 5-axis CNC machining centers.
To reduce costs: try to design axisymmetric parts.
16. Use other machining techniques to replace CNC machining
As said at the beginning of this article, CNC machining is an expensive machining process.
Therefore, no matter how to reduce the cost, the cost is always higher.
In today’s fast-changing modern machining technology, we should think about using other processes to replace CNC instead of solidifying thinking. The previous generation of products used CNC machining, and the new generation of products must use CNC machining.
When the batch is small, the cost of 3D printing is lower than that of CNC machining; when the batch is large, the cost of molding processes such as investment casting and injection molding is lower than that of CNC machining.
The table below shows the process options for different quantities of CNC parts:
| Number of parts | Plastic | Metal |
| <10 | 3D Printing | 3D Printing & CNC |
| 10~100 | 3D printing (consider CNC) | CNC (consider 3D printing) |
| 100~1000 | CNC (considering injection molding) | CNC (considering investment casting) |
| >1000 | Injection Molding | Investment Casting or Die Casting |
As the ancient poem says:
Where there are no herbs in the end of the world, the next craft will be better.
There are many occasions where 3D printing is better than CNC machining:
3D printing can process parts with more complex geometries.
3D printing can provide samples within 24 hours.
3D printing is usually cheaper in small quantities.
3D printing can process materials that are difficult to process by CNC, such as super alloys.
However, CNC machining is also better than 3D printing. When CNC machining different parts and the machining needs of different customers, the selected machining technology will be different. Each machining technology has its advantages and disadvantages. According to different situations and CNC machining needs Choose the appropriate machining technology.
To reduce costs: use other processes instead of CNC machining.
Note: The same is true for any other manufacturing and fastening process, including injection molding, stamping, welding and riveting, etc. When selecting a process at the early stage of product design, choose an appropriate cost-saving process.
last words
Cost reduction design is a very challenging job, and domestic engineers generally lack this knowledge. In my actual product development experience in the first few years, I basically did not consider the cost in the design, and one-sidedly believed that “customer first” and “customer first”, the engineer’s design duty is to meet customer needs, and the cost is handed over to the CNC machining and manufacturing department.
This is a misperception of product cost:
1) Product cost has a very high status in product development
As advocated by product development, product development is an investment behavior. If the cost of the product cannot bring profits or even losses to the enterprise, even if the customer is satisfied with the product, such product development is a waste of corporate capital resources and manpower. resources, which do not produce any value. In this way, the enterprise will eventually be eliminated.
2) More than 85% of the product cost is determined by product design, and the remaining 15% is determined by product manufacturing
If the cost-oriented product design is not carried out in the product design, it is bound to be doomed to be too expensive in the final production of the product. During the transition from “China CNC machining and manufacturing” to “China CNC machining and manufacturing 2025”, cost-oriented product design must be carried out.
To carry out cost-oriented product design, companies and engineers must first change the way of thinking and improve cost awareness, when one day engineers will think about every detail of product design, such as:
1. Should the wall thickness of the part be 4mm or 5mm?
2. Should the rounded corners be designed to be 0.3mm or 0.5mm?
3. Should the important dimensional tolerance be 0.05mm or 0.1mm?
It can be said that engineers have a preliminary cost awareness.
Without such cost awareness, an engineer is not an engineer, just a draftsman who can use Creo, UG or Solidworks.

The above is just a summary of the CNCMF CNC machining factory. If you want to know more about CNC machining, you can contact us: [email protected] to negotiate with us.