What is EDM?
EDM, also known as Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) or EDM, is one of the four most popular CNC machining methods, alongside CNC milling, CNC turning and grinding.
Completely different from the principle of metal cutting, EDM is a process method for machining through the electro-corrosion effect of pulse discharge between the tool electrode and the workpiece electrode. Since sparks can be seen during the discharge process, it is called EDM.
According to different EDM processes, EDM can be divided into EDM wire cutting, EDM perforation forming, EDM grinding and boring, EDM synchronous conjugate rotary machining, EDM high-speed small hole machining, EDM surface strengthening and lettering, etc.
At present, EDM technology has been widely used to process various materials with high melting point, high strength and high toughness, such as hardened steel, stainless steel, die steel, cemented carbide, etc., as well as parts with complex surfaces and special requirements such as molds.
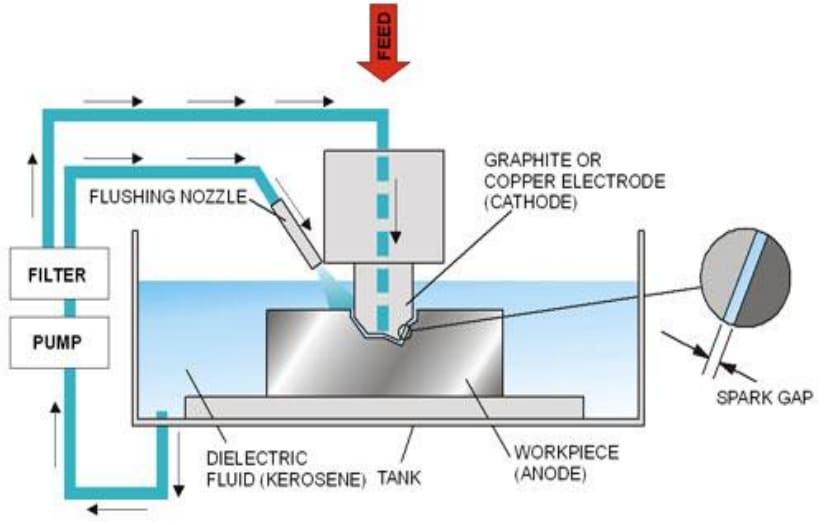
In this article, we’ll examine how it works, its benefits, and its processing limitations and applications. let’s start!
The basic principle of EDM
The principle of EDM is to remove excess metal based on the electrical corrosion phenomenon of pulsed spark discharge between the tool and the workpiece (positive and negative electrodes), so as to achieve the predetermined processing requirements for the size, shape and surface quality of the workpiece. The workpiece and tool electrodes are respectively connected to two electrodes with different polarities of the pulse power supply. Electrocorrosion-resistant materials such as copper, graphite, copper-tungsten alloy and molybdenum are commonly used for tool electrodes with good electrical conductivity, high melting point and easy processing. During the machining process, the tool electrode is also lost, but it is less than the amount of metal removal of the workpiece, and even close to no loss.
As a discharge medium, the working fluid also plays the role of cooling and chip removal during the processing. Commonly used working fluids are mediums with low viscosity, high flash point and stable performance, such as kerosene, deionized water and emulsions. CNCMF is a machining factory with more than ten years of CNC machining experience. It has complete equipment, CNC turning/milling/grinding/drilling/machining. Partners who have parts processing needs are welcome to call for quotation.
When a pulse voltage is applied between the two electrodes, when a proper gap is maintained between the workpiece and the electrode, the working fluid medium between the workpiece and the tool electrode will be broken down to form a discharge channel.
Instantaneous high temperature is generated in the discharge channel, which melts and even vaporizes the material on the surface of the workpiece, and also vaporizes the working fluid medium, which rapidly thermally expands and explodes at the discharge gap. Electrical pits.
After the pulse discharge ends, after a period of time, the working fluid is restored to insulation. The pulse voltage acts on the workpiece and the tool electrode repeatedly, the above process is repeated continuously, and the workpiece material is gradually eroded away.
The servo system continuously adjusts the relative position of the tool electrode and the workpiece, and automatically feeds it to ensure the normal pulse discharge until the required parts are processed.
Advantages of EDM
EDM does not use mechanical energy, does not rely on cutting force to remove metal, but directly uses electrical and thermal energy to remove metal. Compared with CNC machining, EDM has the following characteristics:
①It is suitable for processing materials that are difficult to be processed by traditional CNC machining methods, showing the characteristics of “softness overcomes rigidity”. Because the material removal is achieved by discharge thermal erosion, the processability of the material mainly depends on the thermal properties of the material, such as melting point, specific heat capacity, thermal conductivity (thermal conductivity), etc., and has almost nothing to do with mechanical properties such as hardness and toughness. The tool electrode material does not have to be harder than the workpiece, so electrode fabrication is relatively easy.
② It can process parts with special and complex shapes. Since there is no relative cutting motion between the electrode and the workpiece, there is no cutting force during machining, so it is suitable for low-rigidity workpieces and fine machining. Due to the short pulse discharge time and the relatively small area affected by heat on the machined surface of the material, it is suitable for the processing of heat-sensitive materials. In addition, because the shape of the tool electrode can be simply copied to the workpiece, it is especially suitable for the processing of thin-walled, low-rigidity, elastic, fine and complex-shaped surfaces, such as the processing of complex cavity molds.
③It can realize the automation of the processing process. The electrical parameters in the CNC machining process are easier to achieve digital control, adaptive control, and intelligent control than mechanical quantities, which can easily carry out rough, semi-finishing, and finishing processes and simplify the process. After setting the machining parameters, there is no need for manual intervention during the CNC machining process.
④ It can improve the structural design and improve the craftsmanship of the structure. After EDM, the mosaic and welding structure can be changed to a whole structure, which not only greatly improves the reliability of the workpiece, but also greatly reduces the volume and quality of the workpiece, and can also shorten the mold processing cycle.
⑤ The process route of the parts can be changed. Since EDM is not affected by the hardness of the material, it can be processed after quenching, which can avoid heat treatment deformation during quenching. As in the manufacture of die casting or forging dies, the die can be quenched to a hardness greater than 56HRC.
The limitations of EDM
EDM has its unique advantages, but at the same time EDM also has certain limitations, which are embodied in the following aspects:
① Mainly used for the processing of metal materials. Insulated non-conductive materials such as plastics and ceramics cannot be CNC machined. However, recent studies have shown that non-conductor superhard materials such as semiconductors and polycrystalline diamond can also be processed under certain conditions.
② CNC machining efficiency is relatively low. In general, the processing speed per unit processing current does not exceed 20mm3/(A·min). Compared with machining, the material removal rate of EDM is relatively low. Therefore, machining cutting is often used to remove most of the stock, followed by EDM. In addition, there is a prominent contradiction between CNC machining speed and surface quality, that is, the machining speed is very low during finishing, and rough machining is often limited by surface quality.
③ CNC machining accuracy is limited. There is electrode loss in EDM. Since EDM relies on electricity and heat to erode the metal, the electrode will also suffer loss, and the electrode loss is mostly concentrated in the sharp corners or the bottom surface, which affects the forming accuracy. Although the most recent machine tool products have been able to reduce the relative loss ratio of electrodes to less than 1% during rough machining, and to 0.1% or even less during finishing, the problem of low electrode loss during finishing still needs to be further studied.
④ There are metamorphic layers and even micro-cracks on the CNC machined surface. Due to the instantaneous high heat generated on the machined surface during EDM, thermal stress deformation will occur, resulting in a metamorphic layer on the surface of CNC machined parts.
⑤ Restriction of the minimum corner radius. Under normal circumstances, the minimum corner radius obtained by EDM is slightly larger than the machining discharge gap, generally 0.02~0.03mm. If the electrode is damaged or the translation head is used for processing, the corner radius will also increase, which is impossible to achieve. A true perfect right angle.
⑥ Limitation of external processing conditions. During EDM, the discharge part must be in the working fluid, otherwise it will cause abnormal discharge, which will bring trouble to observe the processing state, and the size of the workpiece will also be affected.
⑦ The “gloss” of the CNC machined surface. The CNC machined surface is composed of many pulse discharge pits. Generally, the surface after finishing does not have the “gloss” after CNC machining, and it needs to be polished to emit “light”.
⑧ CNC machining technical problems. EDM is a highly technical job, and mastery is the key to the success of processing, especially for equipment with a low degree of automation, selection of process methods, selection of electrical standards, electrode clamping and positioning, The monitoring of machining status and the determination of machining allowance have a lot to do with the technical level of the operator. Therefore, the accumulation of experience in EDM is crucial.
The above is the summary of CNCMF CNC machining factory. CNCMF is suitable for CNC machining of any conductive material. In this way, no matter your CNC part requirements and application, we can provide you with better CNC machining, EDM services. Upload your design files now and you will receive an instant quote. All our services are offered at competitive prices.