Quality control and inspection methods in a CNC machining factory are crucial to ensuring that products meet the required standards. Here’s an overview of how CNC machining manufacturers implement quality control measures and testing methods to guarantee product compliance:

1. Advanced Inspection Equipment:
CNC machining factories invest in advanced inspection tools and equipment such as coordinate measuring machines (CMM), optical measurement systems, and surface roughness testers. These tools ensure accurate and detailed measurements of finished parts.
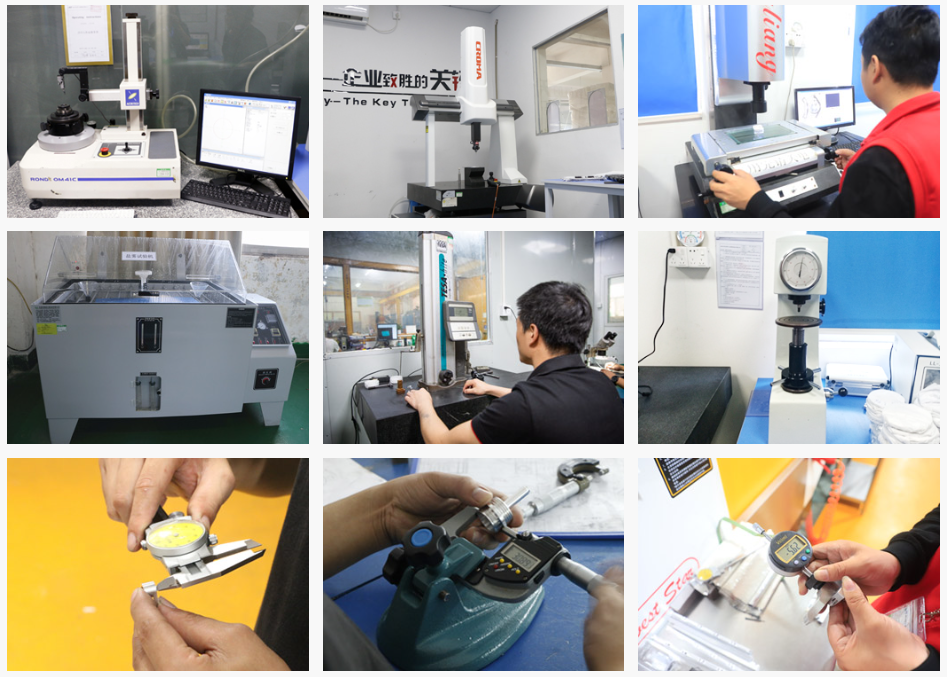

2. In-Process Inspections:
Implement in-process inspections at various stages of production. This includes checking critical dimensions and features during machining to identify and rectify any issues early in the process.
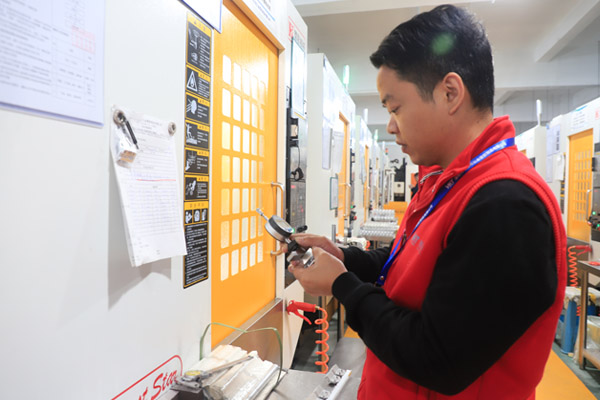

3. Statistical Process Control (SPC):
Utilize statistical process control methods to monitor and control the machining processes. SPC involves collecting and analyzing data to ensure that the manufacturing process remains within specified tolerances.
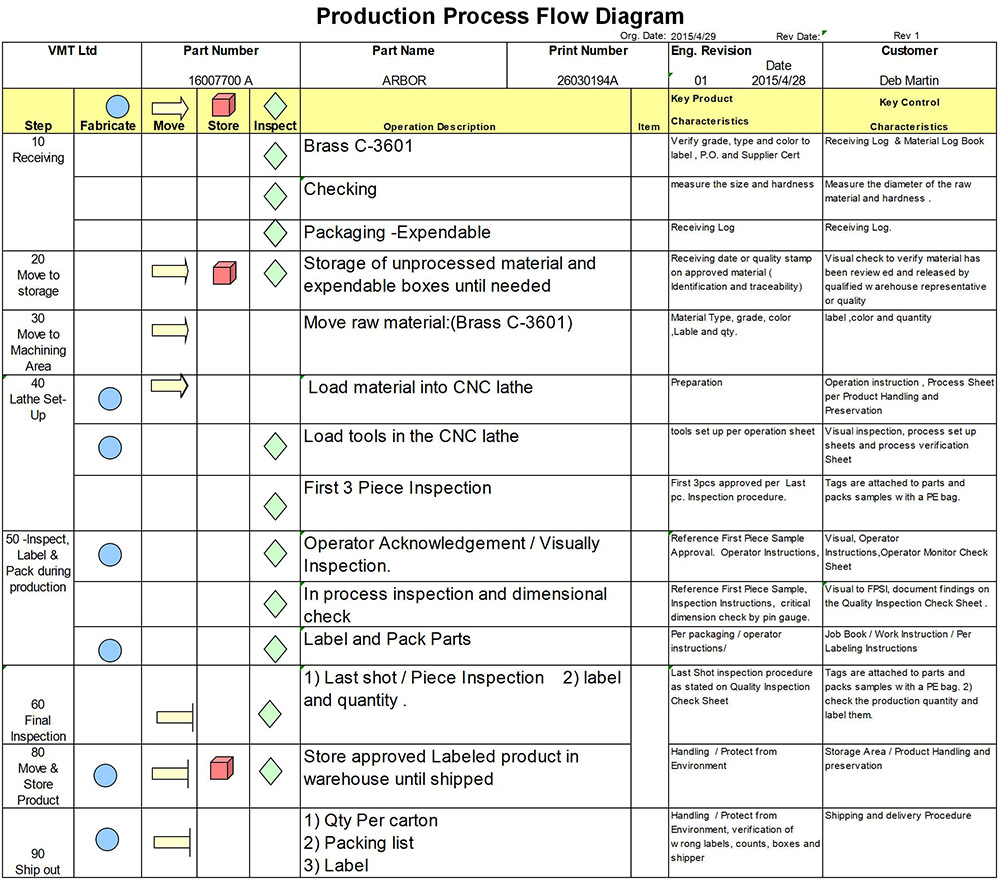
4. Automated Inspection Systems:
Integrate automated inspection systems where possible. Automated systems enhance efficiency and consistency in the inspection process, reducing the likelihood of human error.
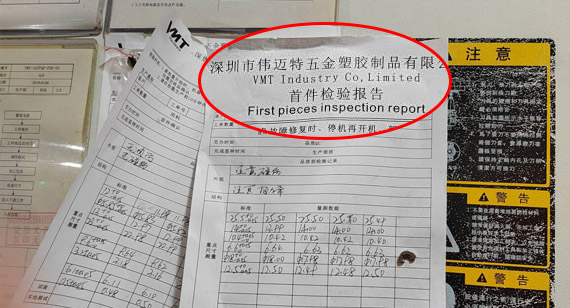
5. First Article Inspection (FAI):
Conduct first article inspections, which involve a comprehensive examination of the first produced part to verify that it meets all specified requirements. This ensures that subsequent parts will be produced consistently.
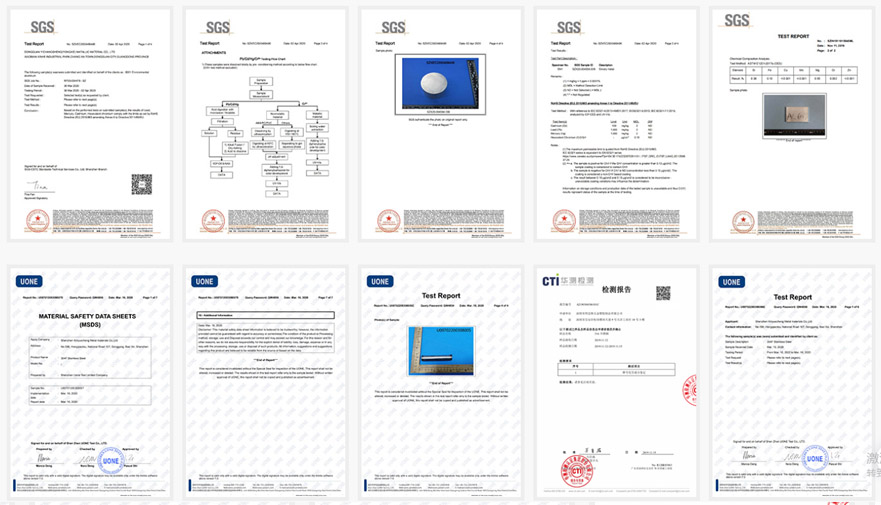
6. Material Testing:
Perform material testing to verify the quality and composition of raw materials before production. This helps prevent defects that may arise from substandard materials.
7. Dimensional Accuracy Checks:
Regularly check the dimensional accuracy of CNC machined parts against engineering drawings and specifications. This ensures that the final product meets the required tolerances.

8. Surface Finish Analysis:
Analyze the surface finish of machined parts using tools such as profilometers. This is crucial for applications where a specific surface quality is required.
9. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT):
Employ non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle inspection, to identify internal defects without compromising the integrity of the part.
10. Quality Management Systems (QMS):
Implement and adhere to quality management systems such as ISO 9001. QMS frameworks ensure that processes are documented, controlled, and continuously improved to meet quality standards.
11. Operator Training and Certification:
Train CNC operators to perform effective quality control checks. Certified operators are equipped with the skills to identify and address issues during the machining process.
12. Traceability and Documentation:
Maintain traceability by documenting and tracking materials, production processes, and inspections. Detailed documentation ensures accountability and facilitates corrective actions if needed.

13. Customer Feedback Integration:
Integrate customer feedback into the quality control process. Continuous communication with customers helps identify specific requirements and ensures that the final product meets or exceeds expectations.
By combining these quality control measures and testing methods, CNC machining manufacturers can confidently deliver products that meet the specified requirements, ensuring precision, reliability, and customer satisfaction.