In daily CNC machining, there will always be quantitative changes in the size of custom CNC parts, tool wear, etc., which leads to errors in CNC parts. In this case, we often need CNC tool compensation to make adjustments. This article mainly describes the relevant knowledge of custom CNC parts tool compensation, if you are interested in this, please read on.
What is CNC tool compensation?
Tool compensation is a processing method to compensate the deviation between the tool used in actual machining and the ideal tool used in programming or the reference tool used in tool setting to ensure that the machining of custom CNC parts meets the requirements of the drawing.
Why CNC tool compensation?
(1) When programming, usually set the position of the tool tip of each tool on the tool post in the CNC part processing position is the same. However, due to the geometry and installation of the tool, the tool tip position is inconsistent, which is relative to the customized CNC part The distance of the processing origin is not the same.
(2) The tool will wear out after a period of use, which will cause errors in the machining dimensions of the custom CNC parts.
(3) The CNC program is generally based on the tool location point and is compiled according to the contour size of the customized CNC part. When the tool tip is not an ideal point but a circular arc, it will cause a position deviation between the actual cutting point and the ideal tool location point.
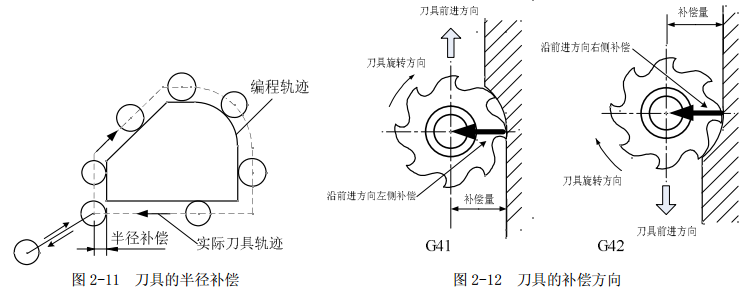
Types of CNC tool compensation
Tool compensation can be divided into two types:
1. Tool offset: geometric position compensation, wear compensation.
2. Tool nose arc radius compensation (can be realized by G41, G42)
Application of Tool Compensation for custom CNC parts
The CNC system has tool compensation function, which can be programmed according to the contour size of custom CNC parts (Note: CNC programming tool cutting compensation is abbreviated as tool compensation, which is mainly used in machining of holes, cavities, and straight positions) , After the tool compensation is established and executed, the CNC system automatically calculates, and the tool position point is automatically adjusted to the tool motion path.
Directly use the custom CNC part size to compile the processing program, the tool wears out, and the processing program does not change when changing, so it is simple and convenient to use. CNC programming tool cutting compensation is abbreviated as tool compensation, which is mainly used in machining of holes, cavities, and straight positions.
(1) Relative compensation application: When setting a tool, determine a tool as a standard tool, and establish a custom CNC part coordinate system based on its tip position A. In this way, when the other tools are turned to the machining position, the tool tip position B will be offset relative to the mark tool tip position A, and the originally established coordinate system is no longer applicable.
(2) Absolute compensation application: when the machine tool returns to the machine zero point, the zero point of the CNC part coordinate system is customized, and the directed distance relative to the position of each tool tip on the tool post. When executing tool offset compensation, each tool sets its own machining coordinate system with this value. The compensation amount can be obtained by measuring with an external tool setting instrument or by trial cutting tool setting.
Therefore, the offset values Δx and Δz between the non-standard tool and the standard tool should be compensated to move the tool nose position B to position A. The standard tool offset value is the directed distance of the zero point of the custom CNC part coordinate system relative to the position of the standard tool tip on the work position when the machine tool returns to the machine zero point.
Summarize
CNC tool compensation is the feed processing route of the CNC lathe. It refers to the path that the turning tool moves from the tool setting point (or the fixed origin of the machine tool) until it returns to the point and ends the processing program, including the path of the cutting process and the cutting and cutting of the tool. Wait for the non-cutting idle stroke path. Therefore, it is necessary to ensure that the custom CNC parts are adjusted when they meet the requirements of the drawings.