Interpolation in CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining refers to the process of calculating intermediate points between two known data points on a trajectory. It involves determining and generating the tool’s path or motion between these points to create a smooth and accurate toolpath for manufacturing.

There are Various Types of Interpolation used in CNC Machining:
Linear Interpolation: It involves creating a straight path between two points. The machine moves the tool at a constant speed in a straight line to reach the end point.
Circular Interpolation: This type generates a curved path between two points. It is commonly used for creating arcs, circles, and other curved shapes.
Helical Interpolation: It involves creating a helix or spiral motion, often used in drilling or creating threads.
Spline Interpolation: Spline interpolation is used to create complex curves. It involves generating a smooth, continuous curve through a set of defined points.
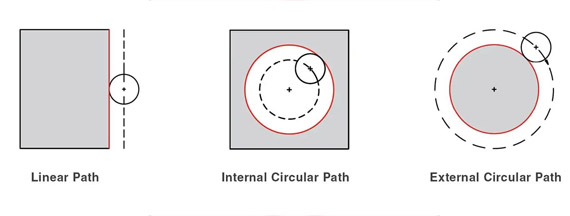
Interpolation plays a crucial role in CNC machining as it determines the accuracy, surface finish, and overall quality of the CNC machining manufacturing parts. CNC machines rely on interpolation to precisely move the cutting tool along the programmed path to produce the desired shapes and features in the workpiece.